Description
Metformin hydrochloride (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide hydrochloride) inhibits the mitochondrial respiratory chain in the liver, leading to activation of AMPK, enhancing insulin sensitivity for type 2 diabetes research. Metformin hydrochloride triggers autophagy[1].
Product information
CAS Number: 1115-70-4
Molecular Weight: 165.62
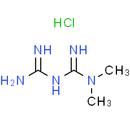
Formula: C4H12ClN5
Synonym:
ADX-155
EFB-0027
EX-404
La-6023
SMP-862
ADX 155
EFB 0027
EX 404
La 6023
SMP 862
ADX155
EFB0027
EX404
La6023
SMP862
Related CAS Number:
657-24-9 (Metformin)
Chemical Name: 1-carbamimidamido-N,N-dimethylmethanimidamide hydrochloride
Smiles: Cl.CN(C)C(=N)NC(N)=N
InChiKey: OETHQSJEHLVLGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChi: InChI=1S/C4H11N5.ClH/c1-9(2)4(7)8-3(5)6;/h1-2H3,(H5,5,6,7,8);1H
Technical Data
Appearance: Solid Power
Purity: ≥98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis)
Solubility: Water: 33 mg/mLwarmed(199.25 mM).
Shipping Condition: Shipped under ambient temperature as non-hazardous chemical or refer to Certificate of Analysis
Storage Condition: Dry, dark and -20 oC for 1 year or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Shelf Life: ≥12 months if stored properly.
Stock Solution Storage: 0 - 4 oC for 1 month or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Drug Formulation: To be determined
HS Tariff Code: 382200
How to use
In Vitro:
Metformin (500 μM) activates AMPK in hepatocytes, as a result, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity is reduced, fatty acid oxidation is induced, and expression of lipogenic enzymes is suppressed. Metformin (2 mM) activates muscle AMPK and promotes glucose uptake. Metformin (500 μM) or AICAR strongly suppresses SREBP-1 mRNA expression in rat hepatocytes. Metformin ameliorates hyperglycemia without stimulating insulin secretion, promoting weight gain, or causing hypoglycemia. Metformin has beneficial effects on circulating lipids linked to increased cardiovascular risk. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production and increases skeletal myocyte glucose uptake. Metformin requires LKB1 in the liver to lower blood glucose levels. Metformin (2 mM) leads to a significant increase in the activity of both α1- and α2-containing complexes in muscle cells. Metformin (2 mM) also increases threonine 172 phosphorylation in muscle cells.
In Vivo:
Metformin (100 mg/ml, po) treatment produces significant decreases in hepatic expression of mRNAs for SREBP-1, FAS, and S14 in SD rats that are consistent with effects documented in cells. Metformin also decreases hepatic lipids in obese mice. Metformin (250 mg/kg, i.p.) increases AMPK phosphorylation in livers of wild-type mice. Metformin (250 mg/kg, i.p.) treatment reduces blood glucose by more than 50% in the wild-type mice on a high-fat diet. Metformin (250 mg/kg, i.p.) treatment also loweres blood glucose in the ob/ob mice by 40%.
References:
- Fryer LG, et al. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(28), 25226-25232.
- Shaw RJ, et al. Science, 2005, 310(5754), 1642-1646.
- Zhou G, et al. J Clin Invest, 2001, 108(8), 1167-1174.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.