Description
Moxifloxacin is a fourth-generation synthetic fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent. Its antibacterial spectrum includes enteric Gram-(−) rods (Escherichia coli, Proteus species, Klebsiella species), Haemophilus influenzae, atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Legionella), and Streptococcus pneumoniae, and anaerobic bacteria. It differs from earlier antibacterials of the fluoroquinolone class such as levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in having greater activity against Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes. Because of its potent activity against the common respiratory pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae, it is considered a "respiratory quinolone."
Product information
CAS Number: 186826-86-8
Molecular Weight: 437.89
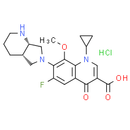
Formula: C21H25ClFN3O4
Synonym:
BAY12-8039
BAY 12-8039
BAY-12-8039
BAY128039
BAY-128039
BAY 128039
Moxifloxacin
Avelox
Avalox
Avelon
Vigamox
Moxeza
Related CAS Number:
354812-41-2 (Moxifloxacin (free base))
Chemical Name: 7-[(4aS, 7aS)-1, 2, 3, 4, 4a, 5, 7, 7a-octahydropyrrolo[3, 4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride
Smiles: Cl.COC1=C(C(F)=CC2=C1N(C=C(C(O)=O)C2=O)C1CC1)N1C[C@@H]2CCCN[C@@H]2C1
InChiKey: IDIIJJHBXUESQI-DFIJPDEKSA-N
InChi: InChI=1S/C21H24FN3O4.ClH/c1-29-20-17-13(19(26)14(21(27)28)9-25(17)12-4-5-12)7-15(22)18(20)24-8-11-3-2-6-23-16(11)10-24;/h7,9,11-12,16,23H,2-6,8,10H2,1H3,(H,27,28);1H/t11-,16+;/m0./s1
Technical Data
Appearance: Solid Power
Purity: ≥98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis)
Solubility: DMSO 87 mg/mL (198.68 mM) Water 60 mg/mL (137.02 mM)
Shipping Condition: Shipped under ambient temperature as non-hazardous chemical or refer to Certificate of Analysis
Storage Condition: Dry, dark and -20 oC for 1 year or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Shelf Life: ≥12 months if stored properly.
Stock Solution Storage: 0 - 4 oC for 1 month or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Drug Formulation: To be determined
HS Tariff Code: 382200
How to use
In Vitro:
Moxifloxacin exerts its effects by trapping a DNA drug enzyme complex and specifically inhibiting ATP-dependent enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV. Moxifloxacin shows in-vitro potency against M. tuberculosis H37Rv with MIC of 0.177 μg/mL. Moxifloxacin has broad Grampositive and Gram-negative activity. Moxifloxacin shows in vitro and clinical efficacy against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Str. pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Chlamydia pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Moxifloxacin has activity against mycobacteria in addition to M. tuberculosis; Moxifloxacin is more active against M. kansasii than M. avium complex: specifically MIC90 for M. avium > M. intracellulare > M. kansasii at 4, 2 and 2 μg/mL, respectively. MIC90 for M. chelonae > M. fortuitum at 16 and 0.5 μg/mL, respectively.
In Vivo:
Moxifloxacin combined with RIF/pyrazinamide (PZA) reduces treatment time by up to 2 months compared to regimens with isoniazid (INH)/RIF/PZA in a mouse model designed to mimic human disease. Similar results with a stable cure are reached after 4 months in mice treated twice weekly with RIF/Moxifloxacin/PZA compared to cure in 6 months when daily treated with RIF/INH/PZA. 100 mg/kg Moxifloxacin in mice gives activity comparable to INH; increased dose in mice to 400 mg/kg Moxifloxacin daily results in spleen CFU counts lower than for INH 25 mg/kg although the differences are not statistically significant. AUC/MIC ratio correlates best with in-vivo efficacy for the fluoroquinolones in a mouse model of tuberculosis.
References:
- Tuberculosis (Edinb), 2008, 88(2):127-131.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.